Dominion Engineering, Inc. Applied Engineering & Research Center is a sophisticated facility where we conduct experimental testing and applied R&D to complement our engineering consulting services. The facility includes a radioactive material handling license, a 30-ft high bay area with 3-ton overhead crane, and 13 MW of backup power to support large scale and mission-critical test programs, and assembly and checkout of nuclear field service equipment. The facility is also fully-equipped with a variety of autoclaves, test loops and compositional and metallurgical instrumentation to support our project activities. Along with our unique blend of practical industry experience and deep scientific expertise, Dominion Engineering, Inc. experimental and research capabilities add a unique and value-adding dimension to our engineering consulting services. Dominion Engineering, Inc. experimental and R&D strengths include:

Independent Process Qualification: Recently, a significant steam generator (SG) sleeving program was implemented by a non-US utility to extend the life of their SG fleet until systematic SG replacement could be performed. In support of local regulatory requirements, Dominion Engineering, Inc. performed independent analysis and qualification of the sleeving process. Specific assistance and insights provided by Dominion Engineering, Inc. included:
These technical justifications supported acceptance of the proposed sleeving process by the local nuclear safety regulator, and the process has been successfully applied without issue at a number of units within the non-US utility’s fleet.
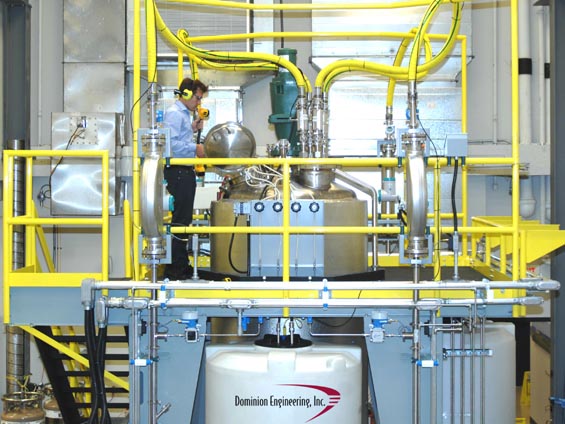

Multi-physics Modeling & Experimental Validation: Some nuclear waste streams exhibit unusual rheological properties and/or contain abrasive minerals that challenge design and reliable operation of processing equipment. Dominion Engineering, Inc. has provided ongoing technical consulting for the Hanford waste treatment plant (WTP) to ensure that waste processing does not result in erosion/wear that exceeds allowances for processing equipment. Dominion Engineering, Inc. technical support provided in this project included:
These results were essential in technical issue closure for erosion/wear at the Hanford WTP.

Crevice Corrosion Modeling & Experimental Validation: When building a new reactor or pursuing license renewal, critical cabling, instrumentation and connectors used within the plant must be qualified or re-qualified to withstand accident conditions, even after thermal and radiation aging during normal plant operation. Dominion Engineering, Inc. was recently contracted to perform a root cause investigation when unexpected failure of a cable/connector assembly was observed in equipment qualification (EQ) testing. Dominion Engineering, Inc. technical consulting services included:
The design / material changes recommended by Dominion Engineering, Inc. were incorporated and facilitated successful qualification of the cabling/connector assembly. The component has since been incorporated into several new reactors and has operated without issue.
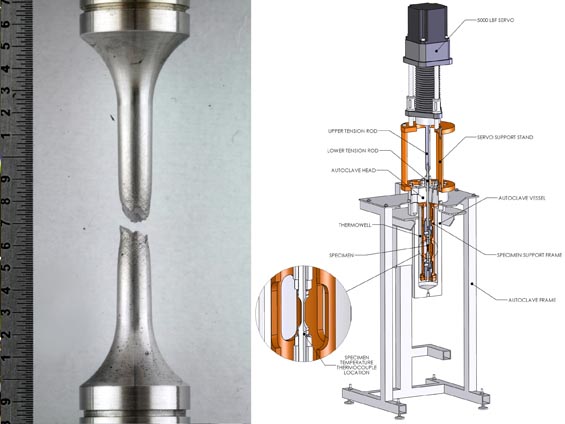
Accelerated Degradation Testing: To guide material selection for an advanced reactor component, Dominion Engineering, Inc. conducted slow strain rate testing (per ASTM G129) of candidate alloys on behalf of the reactor supplier. This accelerated testing method involves slowly straining (10-4 to 10-7/s) axially-loaded test specimens to failure in a test environment in order to evaluate susceptibility to environmentally-assisted cracking. Dominion Engineering, Inc. provided the following technical services in this project:
Dominion Engineering, Inc. material consulting and testing assisted in finalizing and qualifying material selection for the component of interest, which has since been incorporated into the advanced reactor design.
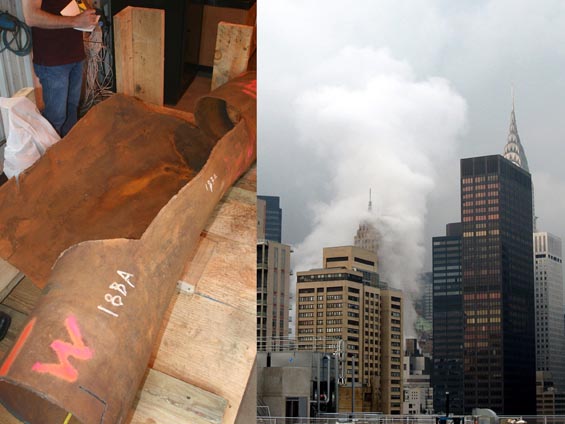

Root Cause Failure Analysis and Metallurgical Examinations: Over the last 30 years, more than 10 steam pipe explosions have occurred within NYC’s underground steam system, which provides heating and cooling for buildings and businesses in Manhattan. Following an explosion near Grand Central Terminal in 2007, Dominion Engineering, Inc. served as a technical expert to evaluate the root cause. Specific Dominion Engineering, Inc. consulting services and insights provided as part of this project included:
Dominion Engineering, Inc. technical breadth and depth was essential for comprehensive support of the investigation process by a single organization, and helped identify the relevance and interplay between different engineering factors.